Use in the Classroom
-
Describe the Purpose
- General Overview: The value proposition must first define the motivation for implementing VPC practises, as well as the difficulties that must be solved. The fundamentals of a proposition are simple to comprehend, such as why a customer should buy a product or service from a specific company. A value proposition should clearly explain how a product meets a need, communicate the intricacies of its added advantage, and explain why it is superior to competing solutions. The optimal value offer is short and to-the-point, appealing to a customer’s most important decision-making factors.
-
Classroom Activity:
A quick, ten-minute summary of the VPC topic should be given at the start of the class lecture, restating the course’s objectives, and summarising the VPC idea. "What do you mean by marketing strategy?" and "How important is a company’s brand to consumers?" are examples of questions that the teacher can ask the students. Some students may choose to volunteer their responses. Teachers must then form groups of 4 to 5 students utilising the knowledge gained above.
- As an activity, provide each group a list of organisations from which to choose, organisations that are directly relevant to marketing strategy.
- The goal of this classroom activity is for students to engage a group discussion within themselves to comprehend and describe the problem of why a particular organisation chose to use VPC. What made them a virtual private server provider? What aspect(s) of VPC does the organisation address, and how? Each student in the group can learn about the organisation by researching their website, the internet in general, and so on during this phase of the group-based activity. Each group can finish this conversation in 30 minutes.
-
Implement the Tool
-
General Overview:
Once the purpose and problem are clearly comprehended, the next stage is to identify the type of actions (or the questions you may want to ask) that relate to implementation of VPC:
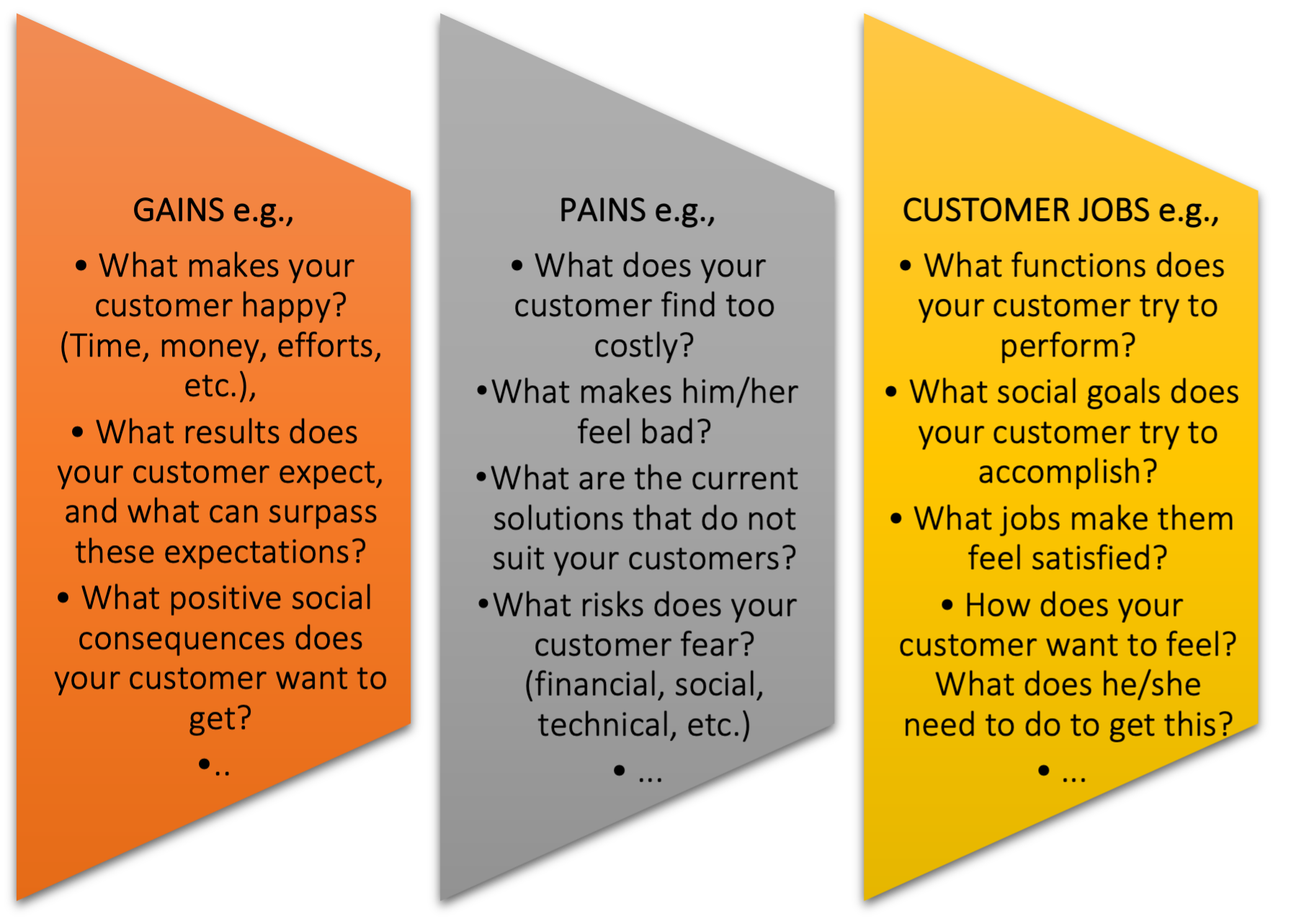
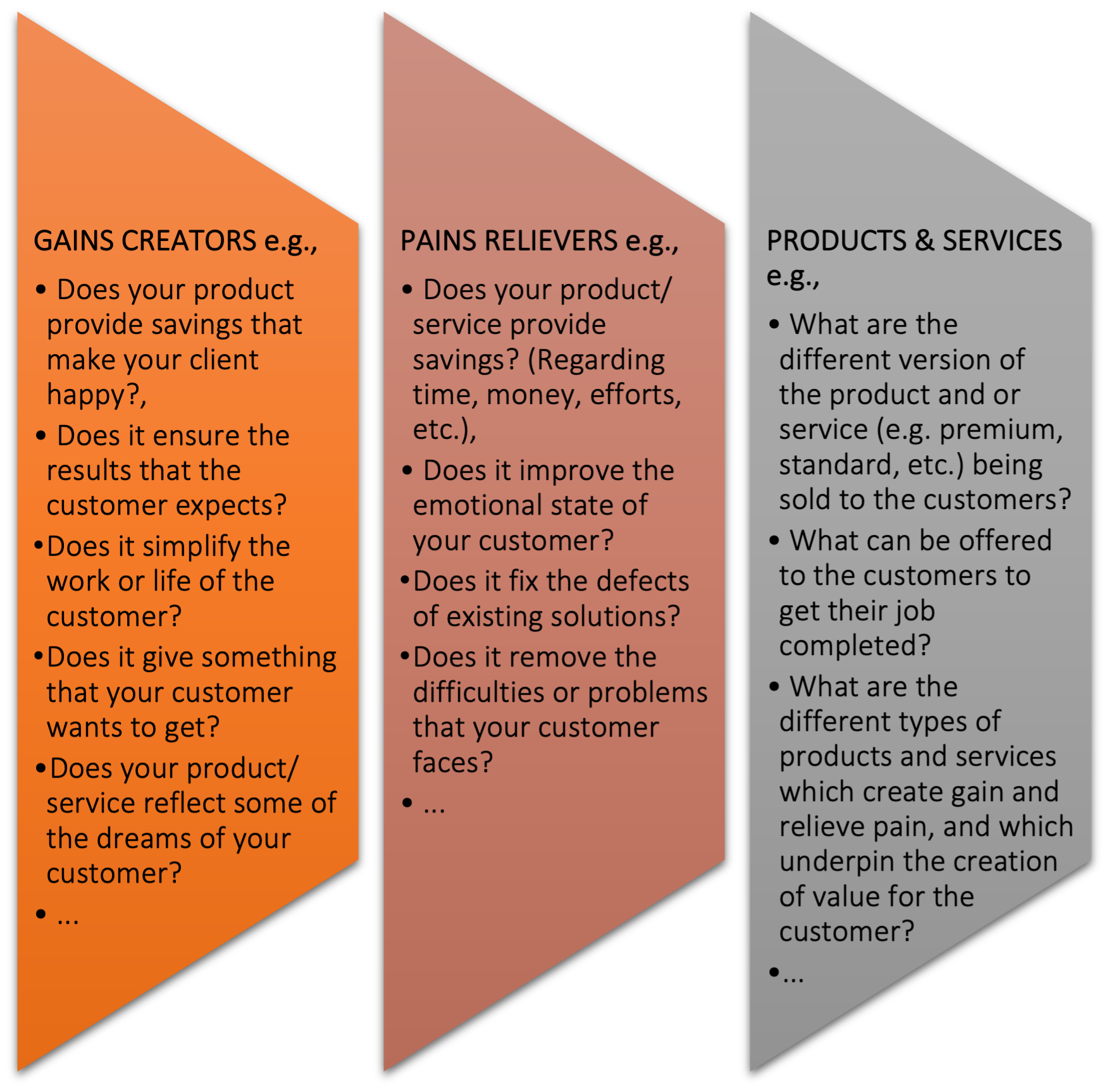
- Classroom Activity: After students have researched the organisation’s website or the online in general, investigated and understood their shift to VPC, they can begin debating and composing topics relating to the organisation using example questions like those shown in Figure 4. After the students have produced their ideas, the HE teacher can request that each group share their findings to the entire class. For their argument to make sense and flow, the students in the group can share (his/her) thought. They can then determine who will take the lead in presenting the findings. Each group can have a 10-minute presentation slot. Students can also share their findings by determining the potential positive and negative effects of general infrastructure on VPC.
-
General Overview:
Once the purpose and problem are clearly comprehended, the next stage is to identify the type of actions (or the questions you may want to ask) that relate to implementation of VPC:
-
Collect Data after Tool Implementation
- General Overview: Once leadership implements VPC practices in its true sense, they can consider evaluating each department’s positioning, resulting in collecting data (either via survey, focus groups, or interviews) to understand the outcomes of implementing VPC.
- Classroom Activity: Once all the groups in the classroom have presented their findings related to their chosen organisation, the teacher can collate the main points presented by each group, either by creating a self-constructed questionnaire or merely extract main points from their presentation of the tool.
-
Analyse the Data and Reflect on the Outcome
- General Overview: Once data is collected, creating, and delivering value proposition is the next step towards the planning strategy.
- Classroom Activity: After aggregating the major points from the group presentations, the teacher has the option of providing feedback to each group after they have given, or allowing all the groups to present, collating the important points, and then providing feedback to each group at the conclusion. In either case, the teacher must provide feedback on the students’ performance during the task. The teacher and students may have a dispute in this final section of the activity. Depending on the number of groups formed in the first stage, the teacher may opt to divide them into two groups, one to discuss the benefits of VPC and the other to discuss the drawbacks. Each faction can strive to persuade the opposite side to agree with their viewpoint. The goal of this group exercise is to assist participants comprehend and appreciate the overall value of VPC.
To summarise, a VPC framework works best in clearly defining what does target customer segment needs, and how a specific product and or service can satisfy their wants.